An vital software for writing high quality Android apps is a set of automated Unit Checks to check your app.
These automated exams have an a variety of benefits, together with:
- They pressure you to grasp the items of performance you’re creating.
- Making an app testable pushes you to have a greater structure in your app.
- They scale back the period of time it is advisable spend on handbook regression testing.
- They will let you do regression testing often — lowering bugs and catching new ones earlier.
- They provide you a software to fearlessly refactor your code because you’ll be assured you haven’t added bugs.
On this tutorial, you’ll modify a Cocktails trivia sport by including unit exams to it.
Automated testing entails a number of several types of testing along with unit testing, so first have a look at how unit testing matches in with different forms of testing.
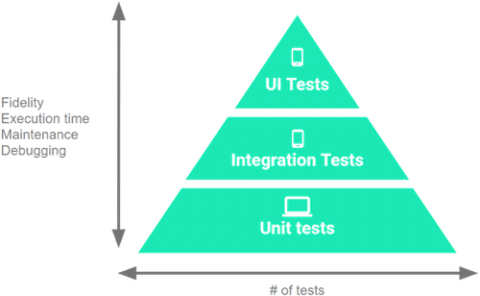
The Testing Pyramid
Checks you may embody in your app’s take a look at suite are categorized into three completely different classes:
-
UI Checks:
These exams work together with the UI of your app. They emulate the person conduct and assert UI outcomes. These are the slowest and most costly exams you may write as a result of they require a tool/emulator to run. On Android, probably the most generally used instruments for UI testing are Compose Take a look at, Espresso, and UI Automator. -
Integration Checks:
Use these when it is advisable verify how your code interacts with different elements of the Android framework however with out the complexity of the UI. They don’t require a tool/emulator to run. On Android, the commonest software for integration testing is Robolectric. -
Unit Checks:
The system below take a look at (SUT) is one class and also you focus solely on it. All dependencies are thought of to be working accurately (and ideally have their very own unit exams :]), so that they’re mocked or stubbed. These exams are the quickest and least costly exams you may write as a result of they don’t require a tool/emulator to run. On Android, probably the most generally used instruments for unit testing are JUnit, Mockito, and MockK.
As a basic rule, it’s best to intention to have the next cut up between the take a look at classes in your venture:
- UI Checks: 10%
- Integration Checks: 20%
- Unit Checks: 70%
As a result of the talents wanted to write down Unit Checks present the foundational expertise for writing Integration and UI exams, this tutorial will give attention to them.
Word: This tutorial assumes you could have earlier expertise with creating for Android in Kotlin, and that you’re conversant in utilizing Compose and Kotlin corountines. In the event you’re unfamiliar with the language, take a look at this tutorial. In the event you’re starting with Android, take a look at a few of our Getting Began and different Android tutorials.
Getting Began
Obtain the supplies for this tutorial by clicking the Obtain Supplies button on the high or backside of the tutorial. Then, open the starter venture in Android Studio Hedgehog or later.
You’ll work with a Cocktails trivia sport that reveals varied cocktails and asks you to guess the title of them.
Construct and run. Right here’s what you’ll see:
The venture accommodates a variety of elements, together with:
- MainActivity.kt: Accommodates the primary exercise for the app.
- CocktailsComposable.kt: Accommodates the composables for the app.
- CocktailsViewModel.kt: The ViewModel to bind the view to the sport, and information.
- Recreation.kt:This holds the info for the sport in addition to some helper strategies to carry out actions within the sport. Positioned in sport ▸ mannequin.
- Query.kt: Holds information a few query and has summary strategies for answering a query. Positioned in sport ▸ mannequin.
- Rating.kt: Class for holding the rating and incrementing it when a query is answered accurately. Positioned in sport ▸ mannequin.
The ultimate app will do the next:
- Load a listing of cocktails from the web.
- Generate questions from that checklist and retailer them within the
Recreationobject. - Retrieve the primary query and current it to the person.
- Enable the person to pick what the reply is to which cocktail they assume it’s.
- Increment the rating if the person’s reply is appropriate.
Elements You Shouldn’t Unit Take a look at
The very first thing it is advisable take into account when testing is that if a element you’re engaged on can’t or shouldn’t be unit examined.
If a element falls into certainly one of these classes, it’s not an excellent candidate for unit testing:
- It has dependencies on the Android Subsystem.
- It has dependencies on an exterior element with a fancy interface.
- The logic within the element can’t be moved out into one other object that doesn’t have dependencies on Android elements.
Within the starter venture, three information clearly fall into these classes:
- MainActivyt.kt: An exercise is tied to the app lifecycle and Android subsystem.
- CocktailsApplication.kt: An app class has many dependencies on the Android subsystem.
The lack to unit take a look at logic in these information is likely one of the causes that good structure patterns suggest breaking out logic into different elements. As you construct the performance in your app, you’ll find out about issues that make a element an excellent candidate to check.
Writing Your First Unit Take a look at
Getting Context
As a primary step, you’ll implement the performance to show a query. This app makes use of Compose views. Open the CocktailsComposable.kt file and take a look at what it’s doing. This accommodates the whole interface you’ll want in your app. You’ll must implement the logic in your viewmodel to present it the info it wants. Look in the course of CocktailsScreen, the primary composable within the file, and also you’ll see:
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
cocktailsViewModel.initGame()
}
That’s the entry level in your viewmodel. Now, search for a couple of strains and also you’ll see this:
val query = cocktailsViewModel.query.collectAsState().worth
That is getting a reference to the present query in a StateFlow from CocktailsViewModel to make use of in the remainder of the display screen.
Now open CocktailsViewModel. Presently, your viewmodel isn’t doing loads, however some helpers have already been supplied for you. Everytime you play a sport, a brand new Recreation object is created. Open the Recreation.kt file situated in sport ▸ mannequin.
The 2 vital issues in your first process are your checklist of questions and your helper methodology to get the following query which you’ll want to make use of in your viewmodel. nextQuestion() is at present not carried out, so that you’ll begin writing a unit take a look at for this.