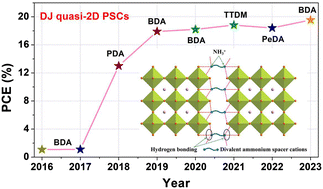
With the advance of nanotechnology, the previous couple of years have witnessed the quick growth of quasi two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites, which exhibit excellent long-term stability in opposition to moisture and warmth, in contrast with their three-dimensional (3D) counterparts. As one of the vital widespread buildings in 2D halide perovskites, quasi-2D Dion–Jacobson (DJ) perovskites present multiple-quantum-well buildings with n layers of [BX6]4− octahedral inorganic sheets sandwiched by two layers of diammonium spacers, thus exhibiting superior structural stability because of the elimination of van der Waals gaps. Due to the achievement of excessive energy conversion effectivity accompanied by spectacular stability, quasi-2D DJ perovskite photo voltaic cells (PSCs) have just lately drawn intensive consideration within the area. This evaluate first introduces the basic understanding of quasi-2D DJ halide perovskites, together with their superior stability, excessive exciton binding vitality, and compositional flexibility and tunable properties. We then summarize detailed methods to organize high-quality quasi-2D DJ perovskites for PSCs, encompassing compositional engineering, solvent engineering, additive addition, and annealing processes. Furthermore, the floor/interface modification and 2D–3D hybrid perovskite heterojunction are additionally mentioned, for offering methods to optimize the fabrication of quasi-2D DJ PSCs. Lastly, present challenges and views towards the long run growth of quasi-2D DJ perovskites for photovoltaics are outlined.